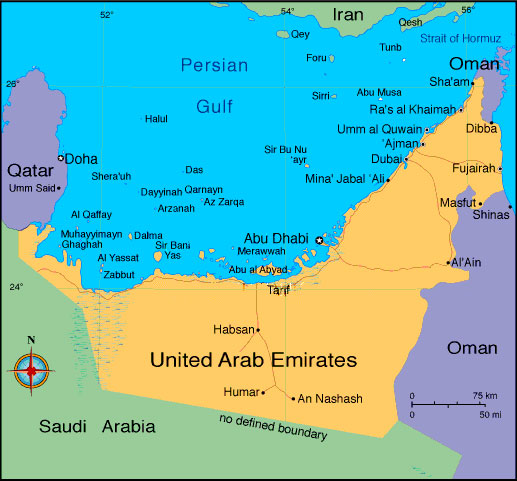
UNITED ARAB EMIRATES
Location: Middle East, between Oman and Saudi Arabia bordering the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf
Capital: Abu Dhabi
Area: 82,880 sq km
Coastline: 1,318 km
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Persian Gulf 0 m
highest point: Jebal Yibir 1,527 m
Official language: Arabic
Population: 2,369,153
Age structure: 0-14 years: 30%
15-64 years: 68%
65 years and over: 2%
Currency: UAE Dirham
Member: Arab League, OPEC, GCC
The United Arab Emirates was created in 1971 as a federation of seven former Trucial States situated in the southernmost part of the Arabian Gulf. The country includes part of the northern Hajar Mountains and also an 80 km stretch of the Gulf of Oman/Arabian Sea coastline directly facing the Indian Ocean. The Arabian Gulf coast of the UAE is about 450 km long, excluding the large collection of islands. Nowhere in the UAE is further than 200 km from shore. Pearl (lulu) fisheries historically contributed to the wealth of the inhabitants of the southern Gulf, but this industry began to decline in 1929.
The Gulf coast is very shallow with numerous inshore and near shore islands. There are some small, entirely man-made islands, and few areas remain completely unaffected by reclamation, dredging, or other development. The islands vary in size from a few tens of square meters to tens of square kilometers. The two largest are Sir Bani Yas and Abu al Abyadh at 220 and over 500 sq km respectively. There are several small islands in the Gulf that are disputed between the UAE and Iran: Abu Musa, Tunb al Kubra and Tunb as Sughra.
The UAE has an area of 83,659sq km and a population over 2million. The official language is Arabic, but due to the large expatriate population, English and Hindi are widely spoken. The currency is the UAE dirham.
Abu Dhabi is the largest of the emirates. Its economy is based on oil revenue (80% of UAE oil).
Dubai lies between Abu Dhabi and Sharjah. It has a major port and duty free zone in Jebal Ali. Dubai is unique in allowing non-native inhabitants to own property and businesses without a UAE partner.
Sharjah has depleted its oil resources. It lies between Umm al Qayweyn and Dubai. It produces textiles and weapons, and in agriculture produces grain, dates, and the traditional pearl diving.
Al Fujieira is located on the Gulf of Oman and is known for its citrus, banana, tobacco and fish.
Ras al-Khaimah is located near the Straits of Hormuz; its industries are farming, fishing and pearl diving.
The smaller emirates have few natural resources and depend on aid from the central government in Dubai. The Emirates are a major tourist and trade region.
The UAE is third in the world in oil reserves (after Saudi Arabia and Iraq), and 4th in natural gas reserves. Other industries are petrochemicals, fishing, construction materials, boat building.
Much of the traditional way of life still survives in the Emirates blended with state of the art technology and large-scale development for which the wealth is used. The communication network is modern, fast and efficient, often lying side by side to traditional seagoing dhows, souqs, bedu camps, camel herds and other typical Arabian sights.
The climate is hot; humid on the coast, especially in summer, but drier inland where the temperatures are even higher. With the Tropic of Cancer passing through the south of the country, summers are long and hot. It usually rains in February or March. The rainfall often takes the form of torrential frontal rain.
The topography of the UAE is characterized by rapid changes between the sand and gravel desert which dominates most of the south and west of the country (and extends inland to the high dune systems of the Empty Quarter, or Rub al Khali, of Arabia), a gravel savannah plain of varying width abutting the western side of the arid Hajar Mountains, which rise to over 1,300 meters, and then, once over the watershed, fall steeply down to the coast of the Gulf of Oman/Arabian Sea. The elevated Musandam Peninsula extending to the Strait of Hormuz is Omani territory.
The Arabian Gulf, on the Eurasian-African flyway, is a staging and wintering area of great importance for migratory birds , shorebirds and other groups of waterfowl. In the UAE, there are internationally important seabird colonies, namely of Socotra Cormorant, Sooty Gull, Great Crested Tern, Lesser Crested Tern, White-cheeked Tern and Bridled Tern, and smaller but nonetheless important numbers of other species such as Western Reef Heron, Osprey and Crab Plover. The bulk of the world population of Socotra Cormorants breeds between the UAE and eastern Saudi Arabia. The birds take advantage of the tidal inlets like Khor Dubai , which are unique to Arabia and the Gulf.
Cities: Ajman, Dubai, Sharjah, Ras al-Khaimah, Abu Dhabi, Fujeira, Umm al-Quwain
Nature reserves: Mushrif National Park
UAE’s Constitution, Universities, Tourism


