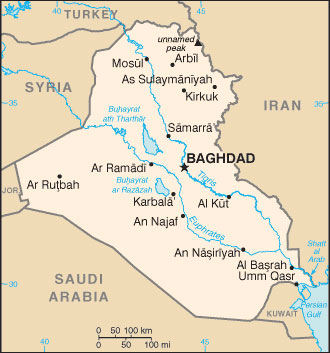
REPUBLIC OF IRAQ
Location: bordering the Persian Gulf, between Iran and Kuwait
Capital: Baghdad
Area: 437,072 sq km
Coastline: 58 km
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Persian Gulf 0 m
highest point: unnamed peak 3,611 m;
(this peak is not Gundah Zhur 3,607 m
or Kuh-e Hajji-Ebrahim 3,595 m)
Official languages: Arabic, Kurdish
Population: 25,374,691
Age structure: 0-14 years: 40.3%
15-64 years: 56.7%
65 years and over: 3%
Currency: Iraqi Dinar
Member: Arab League, OPEC
Iraq is a founding member of the Arab League. It is located in western Asia, bordered on the north by Turkey and Iran, on the east by Iran, on the west by Syria and Jordan, and on the south by Saudi Arabia and Kuwait. It has a narrow access onto the Arabian Gulf through Shatt al Arab; the confluence of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers at the city of Faw.
The country has a population of 24 million and an area of 434,925 sq km. Its capital is Baghdad; the main cities are Mosul, Basra, Najaf, Kirkuk, Kerbala, Samarra, Hilla, Irbil and Suleimaniyeh.
Iraq’s climate is moderately cold in winter, very hot in summer. There is little rainfall in winter except in the northern mountain regions: Sinjar (1543m), and Rawunduz in the (3460m) often see heavy snowfall.
Southern Iraq consists of marshlands called ahwar, which were drained in the 1980s, but an effort to re-flood the land is under way. In the south there only two seasons, winter and summer. In the western region of the country is the Syrian Desert and in the southwest is Samawa, a sand dune desert.
Mesopotamia, the land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers has been inhabited by settled communities since the Sumerians in 4000BC. Other dynasties followed, such as the Akkadian, Assyrian, Babylonian and Chaldean. In the 7th century, Arab Muslims conquered Iraq, and in the 8th century the Abbasid Caliphate established its capital in Baghdad, where Islamic civilization flourished.
The Mongol invasion in 1258 ended the years of prosperity
In 1658 Iraq came under Ottoman rule.
During World War I, British forces invaded Iraq and occupied Baghdad.
It became independent as a monarchy in 1932, and in 1958 a rebellion ended the monarchy and brought the Baath Party into government.
Agriculture products meet the local demand and consist of wheat, barley, rice, vegetables, watermelon, sesame, tobacco, cotton; cattle and sheep. Presently agriculture is a black market industry, production is difficult to estimate. Iraq is the world’s largest producer of dates. Livestock are buffalo, camels, and birds.
Iraq is one of the world’s biggest oil exporting nations, with the world’s second largest proven oil reserves in fields both in the north and in the south of the country.
Iraq’s economy has suffered greatly since the 1980 war against Iran, the economic sanctions after its invasion of Kuwait in 1991, and the US-led war in 2003.
Before the Gulf War in 1991 Iraq exported its oil via:
- a pipeline through Syriato the Syrian port of Banias in Syria ,or to the Lebanese port of Tripoli
- a pipeline to Faw Island on the Arabian Gulf,
- to Silhan across Turkey
Iraq’s main industries are petrochemicals and fertilizers.
In March 2003 the United States declared war on Iraq, claiming the country has Weapons of Mass Destruction. Baghdad fell on 9April 2003, as did the Baath ruling party.
Though no such WMDs were found, Iraq remains under occupation in 2005, with ongoing armed conflict between the occupying forces and insurgents.
Cities: Baghdad, Mosul, Basra, Kerbala, Samarra, Koufa
Nature reserves:
Iraq’s Constitution, Universities, Tourism


