REPUBLIC of SUDAN
Location: northern Africa, bordering the Red Sea, between Egypt and Eritrea
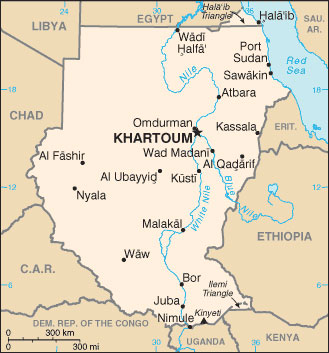
Capital: Khartoum
Area: 2,505,810 sq km
Coastline: 853 km
Elevation extremes;
lowest point: Red Sea 0 m
highest point: Kinyeti 3,187 m
Official language: Arabic
Population: 35,079,814
Age structure: 0-14 years: 45%
15-64 years: 53%
65 years and over: 2%
Currency: Sudanese Dinard
Member: Arab League
Sudan is located in eastern Africa in the Upper Nile basin on the Red Sea. It is bordered on the east by the Red Sea and Ethiopia, on the north by Egypt, on the west by Chad and the Republic of Central Africa, and on the south by Zaire, Uganda and Kenya. Its population is about 30 million.
Its capital is Khartoum (Arabic for “trunk”), named after the shape of the confluence of the White and Blue Nile, where it is situated. Its main cities are Omdurman , Port Sudan, Atraba, al Ubayyid, al Fashir.
It was ruled by Mohammed Ali Pasha in 1820. In 1881 Sudan revolted against the Khedive Ismail. The British invaded in 1898 and annexed Sudan to Egypt, creating the Anglo-Egyptian Sudan. In 1956 Sudan gained independence.
Sudan is the largest country in Africa, covering about 2.5 million km sq, representing 8.3% of the total area of Africa Its terrain is mostly flat plains with hills in the south and southwest and the large Nuba desert in the east, and a fertile plain between the Blue and White Niles called al Jazira. Areas occupied by forests are estimated at 19% of the country area. These forests are diverse in species and diversely used as fuel, timber building material, medicine and for other purposes. Due to lack of alternative energy sources especially in rural areas, trees constitute the main source of energy. This has led to great pressure on forest products and consequently to deforestation and depletion of forest trees.
There are mountains on the east that overlook the Red Sea, and mountains on the south bordering Uganda, where the highest peak is at Kinyeti, at 3187m. Southwest of al Fashir is Jebal Marra, a mountain with a peak at 3088m.
Sudan’s rivers are the Nile and its tributaries: the Blue Nile, Atraba and as Subat, all of which rise in the Ethiopian highlands.
The climate in Sudan is tropical, hot and dry, more moderate on the Red Sea coast where there are popular dive sites.
Sudan is an agricultural country, with cotton the largest export crop. Other crops are white corn, sugarcane, peanuts, wheat, mango, bananas, and sesame. Livestock is a growing sector. The main industries are production of: cotton, textiles, building materials, foodstuffs. In addition to cotton Sudan exports fava beans, and peanuts.
In May 2005 Sudan joined the Convention on Wetlands, the first Wetland of International Importance, effective 7 January 2005, is Dinder National Park.
In recent years Sudan has begun exploiting its small oil resource. Other natural resources are gold, manganese, quartz, marble, copper and salt.
Cities: Atraba, Khartoum, Omdurman, Port Sudan
Nature reserves: Dinder National Park, Radom Park
Sudan’s Constitution, Universities, Tourism


